Understanding Celiac Disease: Navigating Essential Dietary Considerations
Introduction:
Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder where the ingestion of gluten leads to damage in the small intestine. Managing this condition requires careful attention to dietary considerations. Let’s explore essential tips for individuals with celiac disease to maintain a healthy, gluten-free lifestyle.
Gluten-Free Diet: The Cornerstone of Celiac Management:
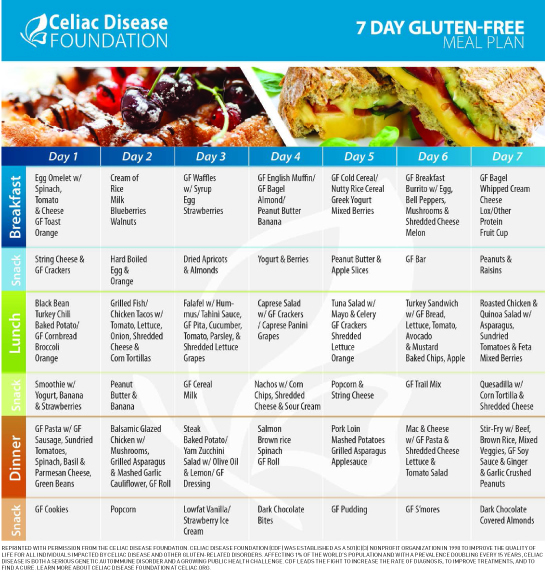
A gluten-free diet is the foundation of managing celiac disease. Gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye, triggers an immune response in individuals with celiac disease, causing damage to the lining of the small intestine. Eliminating gluten-containing foods is crucial for symptom relief and overall well-being.
Navigating Gluten-Free Grains:
While wheat, barley, and rye are off-limits, there are plenty of gluten-free grains and alternatives to choose from. Quinoa, rice, millet, and gluten-free oats are excellent options for incorporating grains into a celiac-friendly diet. It’s important to check labels and ensure that these products are certified gluten-free to avoid contamination.
Mindful Reading of Food Labels:
Individuals with celiac disease must become adept at reading food labels to identify hidden sources of gluten. Manufacturers are required to disclose wheat as an allergen, but other gluten-containing grains may be less obvious. Learning to recognize gluten in its various forms is essential for making informed food choices.
Safe Cooking Practices to Prevent Cross-Contamination:
Cross-contamination is a significant concern for individuals with celiac disease. Even a small amount of gluten can trigger symptoms. Implementing safe cooking practices, such as using separate utensils, cookware, and cutting boards for gluten-free foods, can help prevent accidental exposure to gluten.
The Importance of Gluten-Free Certification:
When choosing packaged foods, look for those with gluten-free certification. This certification ensures that the product meets strict gluten-free standards and has undergone testing to verify its safety for individuals with celiac disease. It provides an extra layer of assurance in avoiding gluten exposure.
Balancing Nutrient Intake:
A gluten-free diet may sometimes lack certain nutrients, such as fiber, iron, and B vitamins, typically found in gluten-containing grains. It’s crucial to balance nutrient intake by incorporating a variety of naturally gluten-free foods, such as fruits, vegetables, legumes, and gluten-free whole grains.
Hidden Gluten in Processed Foods:
Processed foods may contain hidden sources of gluten in the form of additives, flavorings, or thickeners. It’s essential to scrutinize ingredient lists and be aware of potential sources of hidden gluten. Opting for whole, unprocessed foods and cooking from scratch can reduce the risk of unintentional gluten exposure.
Educating Family and Friends:
Living with celiac disease often involves educating family and friends about the importance of a gluten-free diet. Clear communication about dietary restrictions can help create a supportive environment and minimize the risk of inadvertent gluten exposure during shared meals or gatherings.
Regular Monitoring and Follow-Up:
Individuals with celiac disease should undergo regular monitoring and follow-up with healthcare professionals. This includes periodic blood tests and, if necessary, endoscopic examination to assess the healing of the small intestine. Regular check-ups help ensure that the gluten-free diet is effectively managing the condition.
Link to Celiac Disease Dietary Considerations:
For a comprehensive guide on dietary considerations for celiac disease, including tips, recipes, and expert advice, visit Celiac disease dietary considerations. This resource offers valuable insights to support individuals in navigating the challenges of a gluten-free lifestyle.





